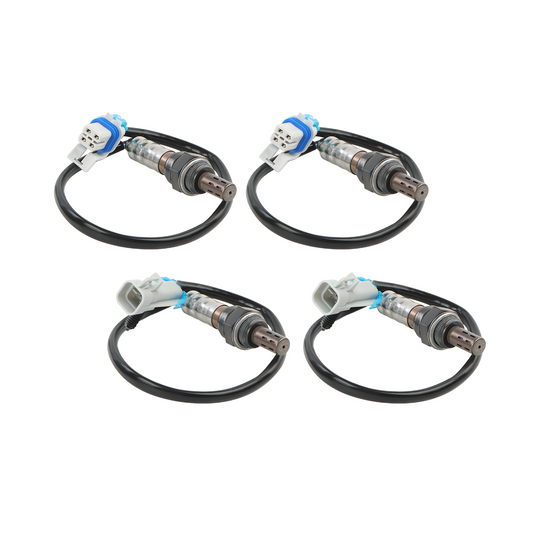
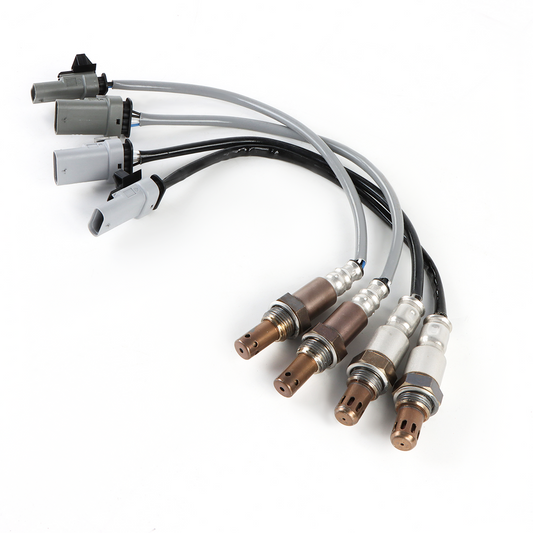
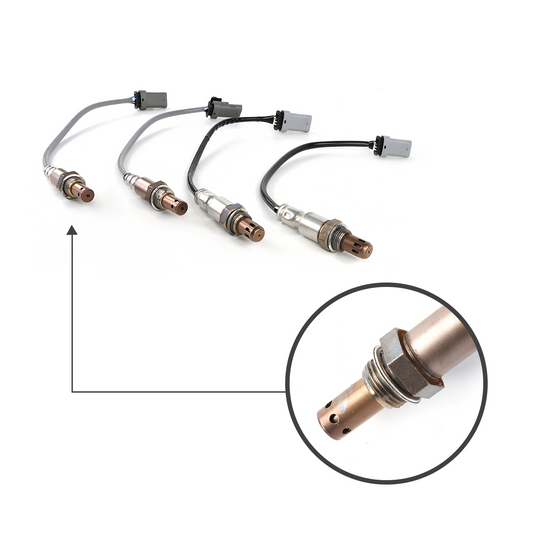
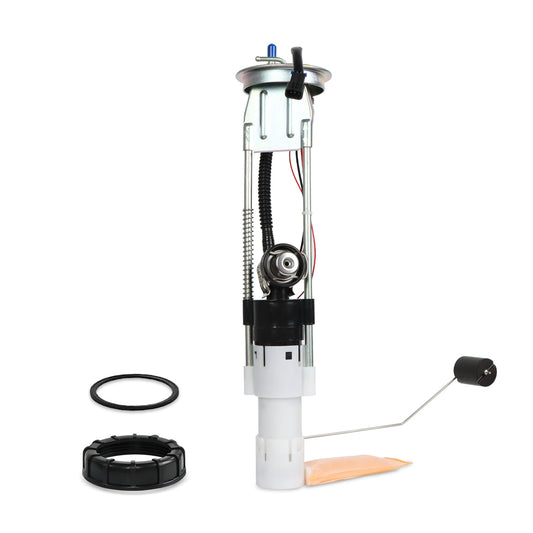
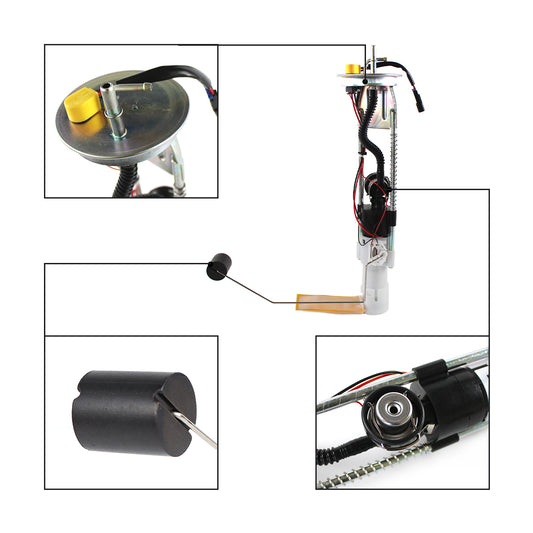
Can I replace an oxygen sensor myself?
19 Jun 2024
Dealing with car problems can be overwhelming, especially when the check engine light illuminates. However, some issues, like a faulty oxygen sensor, can be relatively simple to address. This holds especially true if your automobile has around 100,000 miles on it or more. Oxygen sensors generally have a lifespan of approximately 60,000 to 90,000 miles.
The good news? Replacement oxygen sensors doesn’t present many opportunities to mess up your vehicle. Consequently, you can definitely try and tackle this job yourself to save a few bucks.
Importance of the oxygen sensor
One of the most important sensors in modern cars is the oxygen sensor. Also known as the O2 sensor because O2 is the chemical formula for oxygen, the oxygen sensor monitors how much unburned oxygen is present in the exhaust as exhaust exits the engine. Its primary function is to monitor the level of oxygen in the exhaust gases and provide feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) for optimal fuel-air mixture control. Here are the key functions of an oxygen sensor.
Monitoring air-fuel ratio: The oxygen sensor measures the amount of oxygen present in the exhaust gases. It detects whether the air-fuel mixture is rich (excess fuel) or lean (excess air). This information is relayed to the ECU, which adjusts the fuel injection and ignition timing to maintain the ideal air-fuel ratio for efficient combustion.
Optimizing fuel efficiency: By continuously monitoring the air-fuel ratio, the oxygen sensor helps the ECU fine-tune the fuel delivery. It ensures that the engine operates at its most efficient level, maximizing fuel economy and reducing emissions.
Reducing emissions: The oxygen sensor plays a vital role in reducing harmful emissions. It helps maintain the proper air-fuel mixture, allowing the catalytic converter to effectively convert pollutants into less harmful substances. This control of emissions helps vehicles comply with environmental regulations and reduce their impact on air quality.
Ensuring proper engine performance: A properly functioning oxygen sensor contributes to smooth engine operation. It helps prevent issues like misfires, hesitation, and rough idling by providing accurate feedback to the ECU for precise fuel control. This promotes optimal engine performance and drivability.
Diagnosing engine problems: Except its primary functions, the oxygen sensor can serve as a diagnostic tool. When the sensor detects abnormalities in the air-fuel mixture, it can trigger a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and illuminate the check engine light. This alerts the driver or technician to potential engine issues that require attention and further diagnosis.
Signs You Need a New O2 Sensor
Over time, the O2 sensor can wear out or become contaminated, leading to various issues with your vehicle's performance and fuel efficiency. Here are some signs that indicate you may need a new O2 sensor:

- Check Engine Light: The most common indicator of a faulty O2 sensor is the illumination of the check engine light on your dashboard. When the sensor detects a problem, it sends a signal to the ECU, which triggers the check engine light. However, it's important to note that the check engine light can be triggered by other issues as well, so it's necessary to have the vehicle properly diagnosed.
- Poor Fuel Economy: A failing O2 sensor can cause an imbalance in the air-fuel mixture, leading to decreased fuel efficiency. If you notice a significant drop in your vehicle's gas mileage or find yourself refueling more frequently than usual, it could be a sign that the O2 sensor needs replacement.
- Rough Idle: An O2 sensor that is not functioning correctly can disrupt the engine's idle speed and cause it to run rough or inconsistently when the vehicle is at a standstill. You may experience vibrations, shaking, or even stalling of the engine during idle.
- Engine Misfires: A malfunctioning O2 sensor can result in engine misfires, where the combustion process in one or more cylinders is disrupted. This can lead to a loss of power, hesitation, or jerking sensations while accelerating.
- Increased Emissions: The O2 sensor plays a vital role in controlling emissions by ensuring the proper air-fuel ratio. A faulty sensor can cause an imbalance, even resulting in increased emissions of pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). If your vehicle fails an emissions test or you notice excessive smoke from the exhaust, it may be due to a faulty O2 sensor.
- Reduced Engine Performance: A failing O2 sensor can negatively impact overall engine performance. You may experience a decrease in power, sluggish acceleration, or difficulty maintaining speed. The engine may feel less responsive and struggle to perform optimally.
- Failed Emissions Test: During an emissions test, if the O2 sensor is not functioning correctly, it can lead to a failed inspection. This is because the sensor's readings are used to determine if the vehicle meets the required emission standards.
These signs can also indicate other issues with your vehicle, so it's crucial to have a proper diagnosis performed by a qualified mechanic. They can use diagnostic tools to read error codes and conduct further testing to determine if the O2 sensor is indeed the problem. If you confirm that there is a problem with your oxygen sensor, you will need to replace your car with a new oxygen sensor.
Preparing for the Replacement
Before proceeding with the replacement, it's crucial to identify which oxygen sensor is faulty. Most vehicles have multiple sensors, and determining the specific one that needs replacement will ensure an accurate repair. Here's how you can identify the faulty sensor: Scan for Error Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve error codes from the vehicle's onboard diagnostic system. The scanner will provide a specific code related to the oxygen sensor malfunction. For example, the code P0130 indicates an issue with the upstream sensor in bank 1.
To ensure a successful replacement, it's crucial to acquire a compatible oxygen sensor for your vehicle. Here's what you need to consider:
OEM or Aftermarket: Decide whether you want to purchase an original equipment manufacturer (OEM) sensor from the vehicle manufacturer or an aftermarket sensor from a reputable brand. OEM sensors are designed specifically for your vehicle, while aftermarket options may offer cost savings or additional features.
Sensor Type: Determine the type of oxygen sensor your vehicle requires. Common types include zirconia sensors (most common), titania sensors, and wideband sensors. Consult the service manual or online resources to identify the correct sensor type.
Sensor Position: Identify whether the replacement sensor is upstream or downstream and its specific bank (bank 1 or bank 2). This information ensures compatibility with your vehicle's exhaust system.
Connector Type: Check the electrical connector on the faulty sensor and ensure the replacement sensor has a matching connector. Some sensors may require splicing or adapter kits if the connector differs.
Choose a high-quality sensor from a reputable manufacturer to ensure accurate readings and longevity. As an online store, Daysyore is dedicated to providing high-quality aftermarket auto parts. we are delighted to provide you with the required auto parts products.

Steps of Replacement oxygen (O2) sensor
Replacing an oxygen sensor may seem daunting, but with the correct tools and some basic knowledge, it's a task that can be accomplished in your own garage. Here is a simplified breakdown of the general steps involved in replacing an oxygen sensor:
- Locate the sensor and disconnect the electrical connector: Consult the vehicle's service manual or online resources to find the location of the O2 sensor(s). In most cases, they are located in the exhaust system, either before or after the catalytic converter. Carefully disconnect the electrical connector from the O2 sensor. Some sensors may have a locking tab that needs to be released before disconnecting.
- Remove the old sensor: Use an appropriate wrench or socket to loosen and remove the O2 sensor from its mounting point. Apply penetrating oil if the sensor is difficult to remove due to corrosion.
- Install the new sensor and tighten the sensor: Take the new O2 sensor and ensure it matches the specifications of the old one. Screw the new sensor into the mounting point by hand, ensuring it is aligned correctly. Use the wrench or socket to tighten the O2 sensor snugly but avoid overtightening, as it could damage the sensor or the threads.
- Test the new sensor: Start the engine and check for any warning lights on the dashboard. Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure proper functioning of the new O2 sensor.
If you still have a trouble code related to the oxygen sensor after the repair, it’s possible there’s another problem, and it could be causing readings out of the normal range. Additional diagnosis will be necessary to trace the symptoms to the root.