Development & Principle of Three Way Catalytic Converter
Why is it called a three-way catalytic converter? As the name implies, the three-way catalytic converter converts three pollutants: hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into carbon dioxide (CO₂), nitrogen (N₂), and water vapor (H₂O), which are more commonly found in the atmosphere.
Perhaps this is a bit conceptual, so the following contents will introduce the development of the three way catalytic converter (how it is created and its main purposes), and the principle of it (the process by which it reacts and the factors that affect it) from a full range. If you want to know more, please read on.
Development of the Three Way Catalytic (TWC) Converter
With the development of the contemporary world, people are becoming aware of the importance of environmental protection. One of the major concerns is the emission of automobile emissions.
Although emissions regulations vary significantly in different regions, state governments have enacted laws that strictly control vehicle emissions, both in terms of environmental and health or safety regulations.
Since the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency issued new regulations on exhaust emissions, most gasoline-powered vehicles have been equipped with catalytic converters. Subsequently, three way catalytic converters have been widely used in vehicle emission control systems in the United States. Because they are capable of an additional reduction reaction than two way catalytic converters, and they can purify exhaust gases with maximum efficiency. Even though it is not 100% conversion, it is possible to achieve around 90%, which is sufficient in almost all environments.
As a result, the three way catalytic converter is currently the optimum choice to control emissions in gasoline engines.
Why Do We Need it?
At least in an ideal setting, if there is adequate oxygen, thorough mixing of the fuel and air, sufficient time, and satisfactory high temperature, complete combustion occurs. If not, however, it leads to the production of HC, CO, and NOx emitted directly from the tailpipe into the air.
As is known to all, unburnt hydrocarbons are carcinogenic for people. Carbon monoxide is highly toxic which causes many respiratory diseases. Nitrogen oxides contaminate the natural water cycle and lead to acid rain.
More seriously, these primary pollutants perhaps react with environmental constituents to form secondary pollutants. The secondary pollutants, commonly known as photochemical smog, include O₃, H₂O₂, HNO₃, and more, which are harder to control and cause severe damage to public health.

Then, the purpose of the three way catalytic converter is to minimize these three major pollutants by reacting with waste gases in the exhaust system, thus producing relatively harmless gases expelled into the air instead of emissions of primary pollutants.
That is, the emissions of primary pollutants depend on the air/fuel ratio (A/F ratio). In the combustion process, when the A/F ratio is about 14.7:1, the concentrations of CO, HC, NOx, and O₂ are matched, it ideally achieves complete conversion to produce non-hazardous gases. Nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide are nearly reduced to nitrogen, while hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide are practically oxidized to steam and carbon dioxide. So, the three way catalytic converter is designed to help achieve complete reactions in the ideal state.
How Does the Chemical Reaction Occur?
The numerous chemical reactions in the catalytic converter are able to be classified into four main categories: oxidation, water-gas shift and steam reformation, nitrous oxide reduction, and oxygen storage.
Oxidation
In fact, three noble metals (Pt, Pd, and Rh) all give high activity for oxidation conversion. Among these, carbon monoxide is oxidized to carbon dioxide with the promotion of the Pd catalyst, while the Pt catalyst is mainly responsible for the oxidation of the hydrocarbons. Promoted by the Pt catalyst, hydrocarbons are oxidized to steam and carbon dioxide.
Carbon monoxide oxidation formula:
2CO + O₂ = 2CO₂
Hydrocarbons oxidation formula:
CnHm + (n + m/4)O₂ = m/2 H₂O + nCO₂
Water-gas Shift & Steam Reformation
When there is a lack of oxygen, carbon monoxide reacts with water-gas produced during the combustion, facilitated by ceria, to form carbon dioxide and hydrogen. Similarly, hydrocarbons further undergo a steam reformation to form carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
Water-gas shift formula:
CO + H₂O = CO₂ + H₂
Steam reformation formula:
CnHm + nH₂O = nCO₂ + (n + m/2)H₂
Nitrous Oxide Reduction
Rh is a particularly important catalyst for this reduction reaction. With the promotion of the Rh catalyst, nitrogen oxides are reduced to nitrogen.
Nitric oxide reduction formula:
2NO + 2CO = 2CO₂ + N₂
2NO + 2H₂ = N₂ + 2H₂O
Oxygen Storage
Ceria is an oxygen storage component in the catalyst. When fuel is lacking, the ceria will store oxygen to prepare for reactions and will release oxygen to undergo reactions when it is sufficient.
What Are the Factors that Affect its Work?
Honeycomb Ceramic Monolith
There are two monoliths as the main components of the catalytic converter. One of them is covered with a thin layer of Platinum and Rhodium, and the other with Palladium and Rhodium. However, these three noble metals (Pt, Pd, and Rh) account for only about 1~2% of the total mass of the thin layer.
This thin layer, generally referred to as the washcoat, consists of 70~85% alumina and other oxides, such as BaO and CeO₂. Always, BaO serves as a structural promoter to stabilize the surface area. And CeO₂ (Ceria) goes further than that, it can also be used as a chemical promoter to facilitate reactions during the water-gas and steam reformation, as well as an oxygen-storage component to store and release oxygen depending on fuel-lean or fuel-rich conditions. And the washcoat material is more rough and irregular to increase the surface area, further promoting reactions.
The monolith, composed of cordierite, features well-performed heat conduction. And it offers multiple channels to transport gaseous species with ample concentration to its porous walls, thus accelerating the reaction rate via convection heat transfer. Meanwhile, each channel ensures larger surface areas are exposed to participate in reactions.
Heat-resistant Stainless Steel Body
Heat is generated along with the chemical reactions, which means a protective shield is needed to isolate heat inside. Obviously, stainless steel is the best choice because it is one of the metals with the lowest thermal conductivity and takes longer to conduct heat away from the heat source. That is, stainless steel can not only resist high temperature, thermal shock, and cracking. It can also block heat from diffusion without affecting the work of other vehicle parts.

Summary
As long as air pollution is cut off at the source, environmental problems can be immensely solved. With the advancement of technology and society, carbon emissions are increasingly becoming a more serious issue today. Many new energy companies have decided to replace fuel cars with electric vehicles, but large-scale adoption still has a long way to go. Therefore, the usage of catalytic converters plays a dominant role in emissions even now.
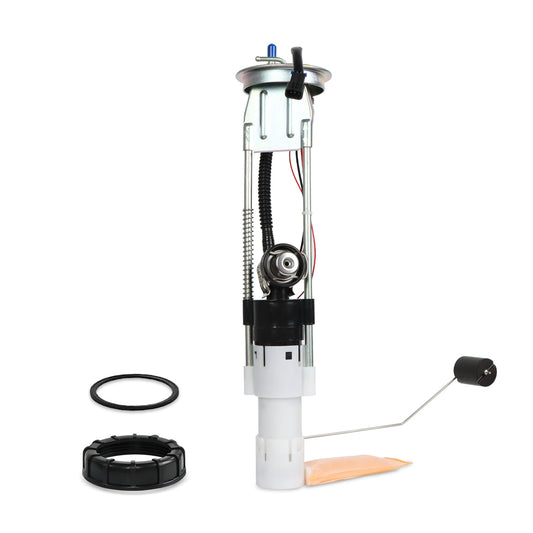
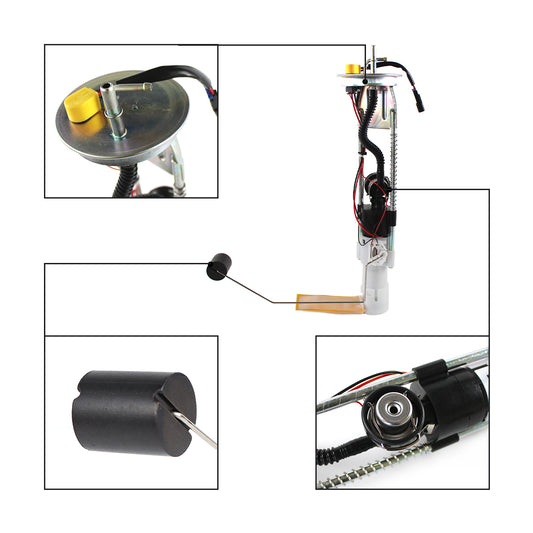
Then, where to find adopted catalytic converters? At Daysyore Auto Parts, there are nine kinds of available models in total, all of which are three way catalytic converters. Besides, we offer honeycomb-like ceramic substrates and a superior stainless steel body to maximize the reaction rates, enabling exhaust gas purification to be achieved to the greatest extent.